05
-
- Introduction to Marketing
- Learning Objectives
● Definition of Marketing
● Differing Business Orientations
● The Marketing Concept - its value and limitations
● Creating customer satisfaction and value
● The Marketing Mix and its limitations -
- What is Marketing - Definitions
- “ the achievement of corporate goals through meeting and exceeding customer needs better than the competition”
(Chartered Institute of Marketing)
“ marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotions and distribution of ideas, goods, and services, to create exchange and satisfy individual and organisational objectives”
(American Marketing Association)
- Shared Points
- ● Marketing is a management process
● Marketing is about giving customers what they want
● Marketing identifies and anticipates customer requirements
● Marketing fulfills customer requirements profitably
- Other Aspects
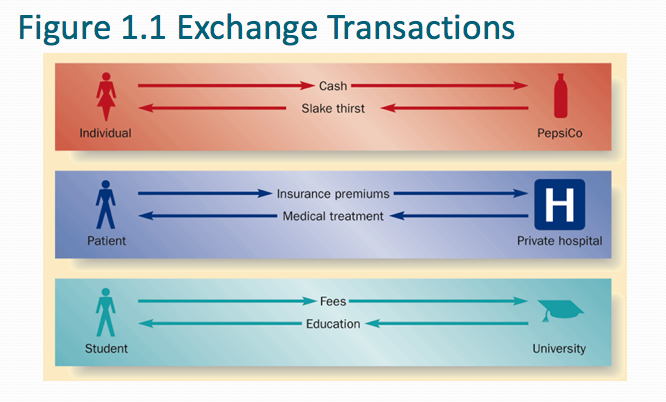
- ● Exchange of ideas, goods, and services
● Pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services
● Relationship marketing -
- Wider Definition of Marketing
- Marketing is to establish, maintain, and enhance relationships with customers and other partners, at a profit, so that the parties involved are met.
This is achieved by mutual exchange and fulfillment of promises.
(Grönroos, 1997)
-
- Sales Orientation
- ● sell what is produced
● consumers needs to be persuaded to buy
● aggressive sales and promotion
● profit through high volume
● Example: Time share holiday homes.
- Marketing Orientation
- ● focus on customers needs
● closer to customers
● profit through customer satisfaction
● Philosophy for the whole organisation
● Development of relationships
● Example: Many successful businesses!
- Differing Business Orientations
- Production Orientation
- ● customer interested in price
● customers price aware
● cost focus
● limited range of products
● Example: Budget Air Travel
- Product Orientation
- ● consumer interest in product
● quality levels of products
● assumption that customers want the product
● Example: Executive Cars -
- The Marketing Concept
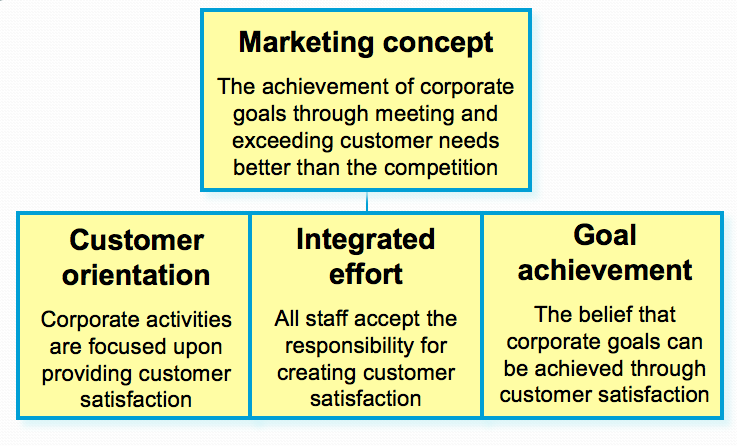
- Emerging Marketing Concepts
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- ● social and ethical marketing
● organisational responsibility to society
● Sustainable marketing
- Electronic Marketing
- ● use of electronic communications technology to achieve marketing objectives
-
- Creating Customer Value
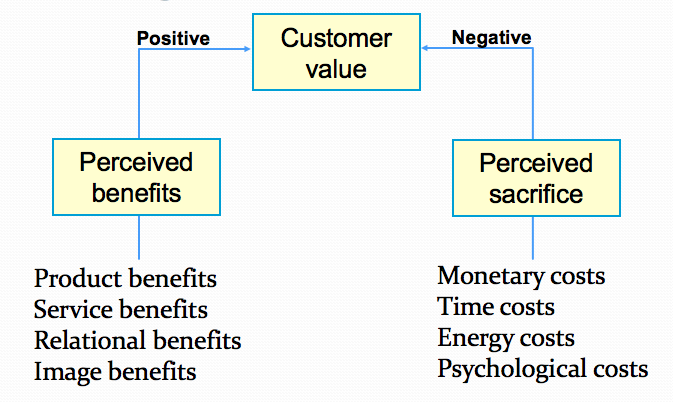
-
Polaroid
Customer Value
Why was the Polaroid Instamatic so popular in Saudi Arabia?

-
- Marketing Management
- ● Identifying customer needs
● Satisfying customer needs
● Strategic vision
● Means by which marketing ideas are turned into reality via the Marketing Mix -
- The Marketing Mix
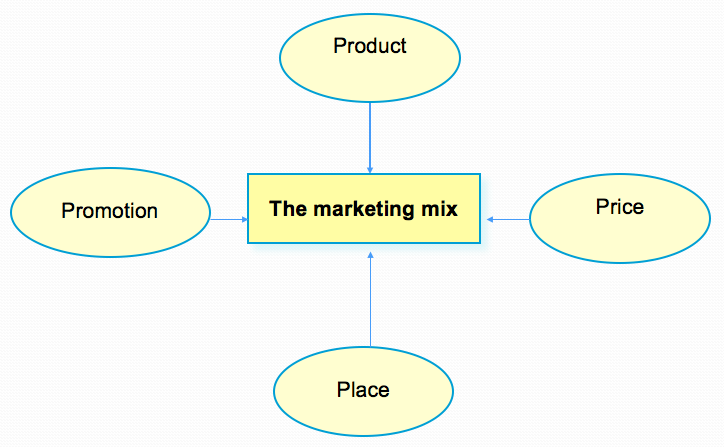
- Promotion
- ● how to communicate with consumers
● advertising
● sales promotion
● personal selling
● public relations
- Distribution / Place
- ● access to target market
● distribution channels
● access to consumers
● retailer image
● logistics
● internet- Marketing Mix 4 Ps
- Product
- ● NPD
● Product Mgt
● goods + extras
● range, features, style
● branding
● packaging
● after sales service
- Price
- ● costs
● profitability
● value for money
● competitiveness
● product worth to the customer
● choice/ quality
- Marketing Mix Services
- ● People - added value and dimension
● Processes - how is service delivered, ensure consistency - queuing mechanisms
● Physical Evidence - tangible and perishable
E.g. a room at the Marriot Hotel for tonight may cost £80. A room at the Marriot Hotel for last night is now worthless!
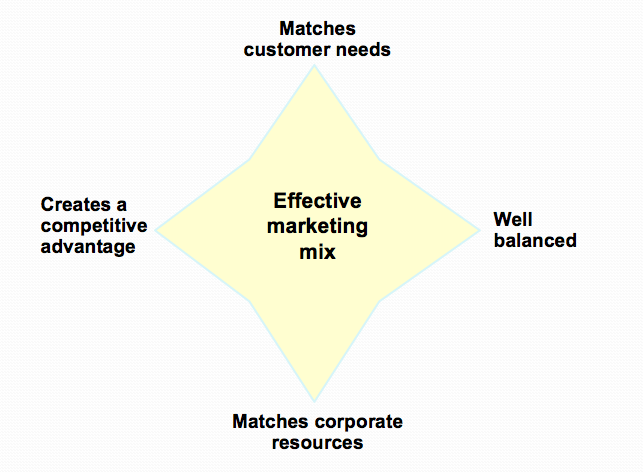
- An Effective Marketing Mix
-
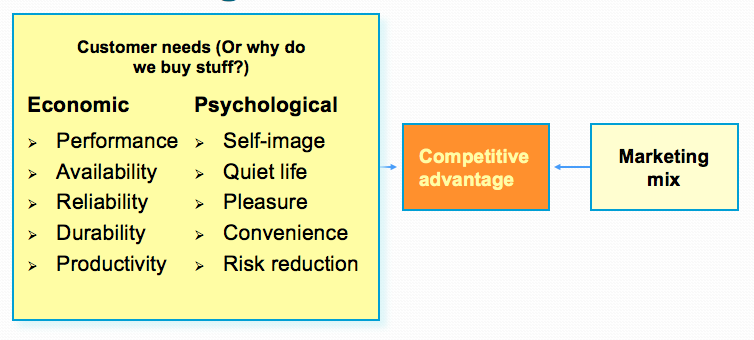
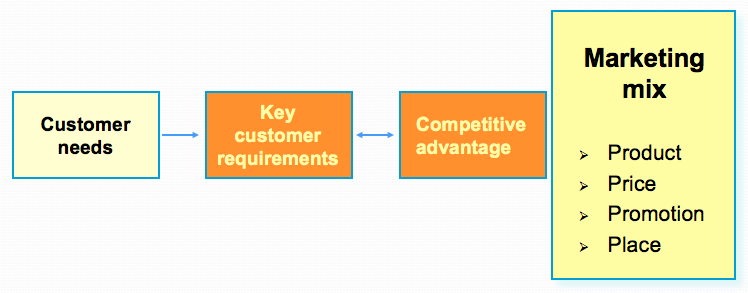
- Marketing Mix and Customer Needs
-
- In Conclusion
- Marketing Myths:
● Satisfied customer = guaranteed loyalty (Ask Nokia)
● Strong Brand is invincible (Ask Blackberry)
● Advertising affects sales (Ask Henry Ford)
Marketing Reality:
● Try to understand what consumers need/want.
● Give it to them effectively
● Build trust and loyalty
● Make money.
-
- Tutorial
- This Automotive tutorial is UK-centric, but similar exercises can be carried out by students of other countries if data is available.