-
PHP and Forms
Submit Button
<input type="submit" /> // defines a submit button
A submit button is used to send form data to a server.
The data is sent to the page specified in the form's action attribute.
The file defined in the action attribute usually does something with the received input
ALWAYS use a Submit Button for Forms in PHP
( For the coursework : ‘Submit’ should ONLY be used for the PHP Form)
Reset
<input type="reset" />
will reset a ‘Submit’ Form
Resets the form to its original position; clears all input fields
- If NOT using ‘Submit’ :
- add a “Clear” button – and add a function to reset each relevant field ( e.g. a clients-side javascript form)
Server Interaction
To interact with the Server ......
Form will contain input fields, e.g. text fields, checkboxes, select lists, submit button etc.
<form action="" method="get" > <input type …/>… </form>
- When the form is submitted (using a SUBMIT button) the data from the input fields is submitted :
- To the URL specified as value of action.
- Using the HTTP method specified as value of method
- e.g. GET or POST.
- There usually is a process set up on the server which “processes” this data.
Get and Post Methods
In simple terms,
- GET method :
- the input values are passed as part of the URL.
- POST method:
- the information is sent to the server as part of the data body and will not be visible in the URL box in the user's browser.
If you don't specify the method, GET is taken by default.
Get Method
<html> <head> <title>Get Ex1</title> </head> <body> <form action="get_Ex1_Result.php" method="get” > Name: <input type="text" name="name"> <br/> <input type="submit" value="Submit" > </form> </body> </html>
$_GET Function
- accesses values sent using the GET method
- e.g $_GET["name"];
- Form or querystring
- Can combine with HTML code ….
Your Name is : <?php echo $_GET["name"]; ?> Welcome <?php echo $_GET["fname"]; ?>. You are <?php echo $_GET["age"]; ?> years old!
values visible in address bar
limited in size
Video
X -
<html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Get Ex1</title> </head> <body> Your Name is : <?php echo $_GET["name"]; ?> <br/> Thanks for using our site <br/> </body> </html>
Get Method …. URL Address
http://localhost:19592 / get_Ex1_Result.php?name=Brian
http://localhost:19592
- get_Ex1_Result.php?name=Brian
- Name of file ? values passed to file
Video
When to use GET?
Can view values – so not very secure
GET may be used for sending non-sensitive data.
Note: GET should NEVER be used for sending passwords or other sensitive information!
But can bookmark page – so can be used for Search
- Can also change values in the URL
- For example – can change ‘name’
<body> <h2> Enter Name and Total </h2> <h2> You will get a 10 pound discount if the total is over 20 pounds</h2> <form action= "get_Ex2_RESULT.php" method= "get“ > Name : <input type="text" name="Name"><br> Total : <input type="text" name="Total"><br> <input type="submit" value="Submit"><br> </form> </body>
<?php $total = $_GET["Total"]; $discount = 10; if (is_numeric( $total )) { if ($total > 20) { $newtotal = $total - $discount; } } else { $newtotal = "invalid "; } ?> <?php echo $_GET["Name"]; ?> .... Thanks for your Order <br/> We can now confirm your discount <br/> <p> Order Total was <?php echo $total; ?> so Discount is ..... <?php echo $discount; ?> New Total is ..... <?php echo $newtotal; ?>http://localhost:19592 /
get_Ex2_RESULT.php ? Name=Brian&Total=30
Can change ‘Name’ And ‘Total’
- Examples of using GET :
- Amazon Search
- Forums
- etc
X -
POST method
The information is sent to the server as part of the data body and will not be visible in the URL box in the user's browser.
Same Structure as ‘GET’ ….- BUT URL is empty
When to use POST?
Information sent from a form with the POST method is invisible to others (all names/values are embedded within the body of the HTTP request) and has no limits on the amount of information to send.
However, because the variables are not displayed in the URL, it is NOT possible to bookmark the page.
Developers prefer POST for sending form data.
POST method
- Will use : 💡 post_Ex1_FORM.php and 💡 post_Ex1_RESULT.php
- Based on : 💡 get_Ex1_FORM.php and 💡 get_Ex1_RESULT.php
Only have to change :
method="get” to ….. method="post"
echo $_GET["name"]; to …. echo $_POST["name"];
Post Method
<form action=“post_Ex1_Result.php" method="post"> Name: <input type="text" name="name"> <br/> <input type="submit" value="Submit" > </form>
Video
Post Method
Your Name is : <?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?> <br/> Thanks for using our site
- URL Address :
- http://localhost:19592 / post_Ex1_Result.php
-> No values displayed – more secure !!
Video
$_REQUEST Function
Can access $_GET, $_POST, and $_COOKIE
Welcome <?php echo $_REQUEST ["fname"]; ?>!<br />
You are <?php echo $_REQUEST["age"]; ?> years old.
- The following files use $_REQUEST:
- 💡 request_Ex1_FORM.php
- 💡 request_Ex1_RESULT.php
PHP_Self
The $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] is a super global variable that returns the filename of the currently executing script.
So, the $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] sends the submitted form data to the page itself, instead of jumping to a different page.
- This way, the user will get error messages on the same page as the form.
- So we can use a single page
X -
htmlspecialchars()
The htmlspecialchars() function converts special characters to HTML entities.
This means that it will replace HTML characters such as < and > with < and >.
- This prevents attackers from exploiting the code by injecting HTML or Javascript code (Cross-site Scripting attacks) in forms.
- Refer to the following for detailed description :
- http://www.w3schools.com/php/php_form_validation.asp
Video
We will examine the various parts of this page :
//htmlspecialchars - This converts HTML tags to special characters //$_SERVER["PHP_SELF - This returns the current filename <form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>"> …. Form fields …. </form>
process Form data
<?php // define variables and set to empty values $Fname = ""; $Sname = ""; $Full = ""; if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") // checks that Form has been submitted - using Submit button { $Fname = $_POST["firstname"]; $Sname = $_POST["surname"]; $Full = "Your Full Name is " . $Fname . " " . $Sname; // create a string - string must be created within PHP code } ?>display values
<?php echo "<h2>Your Details are :</h2>"; echo $Fname; echo "<br>"; echo $Sname; echo "<br>"; echo $Full; echo "<br>"; ?>
Will output each value
Note that the <h2> line will ALWAYS be output
- The other values will ONLY be displayed when they contain text
- That is, when the form has been submitted
PHP Lab
XX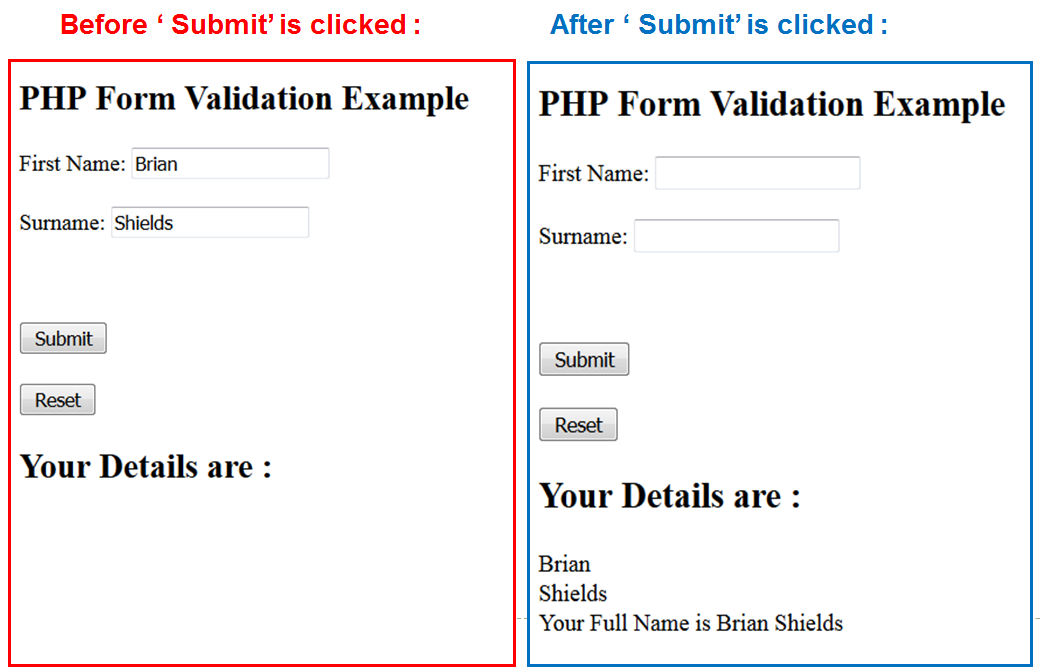
-
PHP Syntax
PHP file (.php) normally contains static html tags with embedded PHP scripting blocks which when executed on server produce html dynamically
A PHP script starts with <?php and ends with ?>
PHP Scripting block:
<?php ... php code ?>
- Semicolons are statement separators
- MUST always use Semicolons !!!!!
- Comments are indicated by:
- // - single line
- /* ... */ - multi-line
Hello World - HelloWorld.php
echo used to output text onto a web page:
<html> <body> <h1> PHP Example (This is HTML ) </h1> <?php echo "Hello World (This is PHP)"; ?> </body> </html>The php file MUST be run on a Web Server to execute the PHP code – e.g WebMatrix
- Note the Server Address – for example :
- localhost:43702/...... /HelloWorld.php
Server Address (URL)
- If it is run on the Client only:
- PHP code will NOT be executed
- Will ONLY view HTML