-
Defining Business Functions
- Represents the logical level structure an organisation uses to control and manage its resource and processes
-
Nature of IT projects
- IT projects can be very diverse, For example:
- Can range in size from small project team installing off-the-shelf hardware & software to large project team analysing several organisations business processes and developing new software
- Can range in technology used
- IT projects can support every possible industry and business function
-
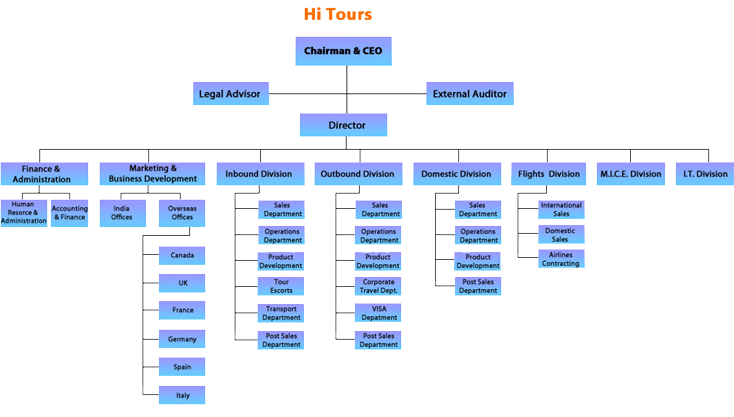
Example Organisation Chart
Additional Information
- If we assume a business function is concerned with governing resources – an organisation chart might be considered the physical implementation of a business function – shows how, via the lines of reporting, the control and management of resources is structured
-
Typical Business Functions
- Production/Operations
- Sales and Marketing
- Human Resources
- Research and Development
- Customer Service
- Finance and Accounts
- Administration
Additional Information
- The functions of a business may be primarily divided into two types called production and marketing. These two functions are mutually dependent.
- Besides the two primary functions, there are a number of assisting functions like accounting, advertisement, financing, staffing, directing and research and development.
- The business, management and operative functions work together to achieve your business objectives and to make it profitable
-
Production and Operations
- Acquiring resources
- Planning output – labour, capital, land
- Monitoring costs
- Projections on future output
- Production methods
- Efficiency
Additional Information
- Production function involves creation of goods and services using resources - money, people and materials. For the purpose of production several processes and techniques are employed. Production functions involve plant location and layout, plant building, production planning, repair and maintenance and quality control. Since production helps in the creation of utilities, this has been considered as the most significant function of the business.
-
Sales and Marketing
- Market research
- Promotion strategies
- Pricing strategies
- Sales strategies
- The sales team
- Product – advice on new product development, product improvement, extension strategies, target markets
Additional Information
- Sales Function
Technology development, globalisation and large buyers contribute to complicate the sales function of a business. To succeed in this environment, the sales function of the business focuses on the customer and building long-term relationships. Its function involves keeping an eye open for new sales channels to reach as many customers as possible while adapting to diverse cultures and languages- Marketing – to generate customers
- Marketing function: Marketing function is primarily concerned with the distribution of goods and services among the people. For smooth marketing of the product, the marketing manager decides on the product, its packing and branding, deciding the distribution channel and promoting the future sales. Marketing functions involve four 'P' like product, price, promotion and physical distribution.
-
Human Resources
- Recruitment and retention
- Job descriptions
- Person Specifications
- Dismissal
- Redundancy
- Motivation
- Professional development and training
- Health and safety and conditions at work
- Liaison with trade unions
Additional Information
- HR or Personnel function: This function is concerned with the human side of the business and concerned with procurement, development and maintenance of efficient and effective work force. The personnel functions include selection, training, promotion, transfer, payment of wages, welfare activities and industrial relation
-
Research and Development
- New product research
- New product development
- Existing product updates
- Quality Checks
- Innovation
Additional Information
- Existing product updates
Existing products of the company also fall under the scope of research and development. The department regularly evaluates the products offered by the company to ensure they are still functional. Potential changes or upgrades are considered. In some cases, the research and development department is asked to resolve a problem with an existing product that malfunctions or to find a new solution if the manufacturing process must change.- Quality Checks
In many companies, the research and development team handles the quality checks on products created by the company. The department has an intimate knowledge of the requirements and specifications of a particular project. This allows team members to ensure the products meet those standards so the company puts out quality products. If the company also has a quality assurance team, it may collaborate with research and development on quality checks.- Innovation The research and development team aids the company in staying competitive with others in the industry. The department is able to research and analyse the products other businesses are creating, as well as the new trends within the industry. This research aids the department in developing and updating the products created by the company. The team helps direct the future of the company based on the information it provides and products it creates.
-
Finance and Accounts
- Cash flow
- Monitoring income/revenue
- Monitoring expenditure
- Preparing accounts
- Raising finance
- Shares
- Loans
- Links with all other functional areas
Additional Information
- Finance function: Looks at how the business uses its money, and what it invests in (projects etc.). It will also consider the return on investments and how to raise capital. Finance is regarded as the life-blood of the business unit. This function involves planning, procurement and effective utilisation of the funds of the business. The Finance department estimates the financial requirements, investment of funds in the short-term or long-term, determining the capital structure and determination of the sources of raising capital.
-
Customer Services
- Monitoring distribution
- After-sales service
- Handling consumer enquiries
- Offering advice to consumers
- Dealing with customer complaints
- Publicity and public relations
Additional Information
- Customer Service is the provision of a service to a customer before, during and after an enquiry/purchase. For example, a Bank may have a Call Centre that deals with customer enquiries. Call Centre staff will be able to handle enquiries about customers accounts, process account transactions, deal with customer complaints and escalate to different teams as required. Customer satisfaction surveys will allow management to monitor the efficiency of the service.
-
Admin
- Managing estates – cleaning, health and safety, maintenance, security
- Reception
- Clerical work – reporting, recording, record keeping, communication
- Overview of quality control
Additional Information
- This can cover the administration of a business/organisation on a day to day basis
-
Characteristics of IT projects: team members job roles
Common job titles:
- Applications: business analyst, systems analyst, project manager, developer (programmer, web developer), database analyst, test analyst, business architect, solutions architect
- Operations: technical support engineer, network engineer, technical consultant
-
Diverse Technologies
- Job titles reflect diverse technologies required for IT projects
- Issues
- Communication: between different job roles can be challenging
- Diverse technologies which can change rapidly
-
Business Analyst (BA)
- The vast majority of business analyst roles deal specifically with software projects
- Business change and software implementations tend to go hand-in-hand
- Some roles focus more on aligning the business team around the scope of a solution, and some focus more on detailed requirements for the technical team to implement.
Additional Information
- Business Analysts (known as BAs) are responsible for analysing a business’s processes and investigating how they work. They then identify improvements that can be made and present the case for these improvements back to the business.
- Although specific responsibilities vary greatly from specialism to specialism, the role of a Business Analyst will generally include the following:
- Analysing the business (either one element or the business as a whole)
- Evaluating all available data
- Identifying any problems that need addressing or potential improvements
- Projecting how feasible these improvements are to make
- Using all of the acquired information to present a business case back to the company which details the solutions
- Implementing the necessary and agreed-to changes, overall increasing efficiency for the business
-
Typical Business-focused role responsibilities – BA role
- Understanding the needs of multiple stakeholders
- Facilitating the negotiation of requirements amongst multiple stakeholders.
- Identifying the current- and future-state business processes
- Helping the business stakeholders envision the future and how their work will need to change to support the future
-
Typical Technology-focused role responsibilities – BA role
- Creating, analysing, and validating detailed functional specifications
- Facilitating design sessions with the implementation team to define the solution
- Delivering elements of systems design, including data migration rules, business rules, wireframes, or other detailed deliverables
-
Systems Analyst role
- examining current systems
- talking to users (requirements gathering)
- producing specifications for new or modified systems
- liaising with other IT staff such as programmers (application developers) to produce new systems
- implementing new systems
- They are also responsible for user training and feedback
Additional Information
- The skills of systems analysts are called upon when operational problems are encountered with IT systems. Typical duties include the above.
-
Applications Developer role
- Translate software requirements into workable programming code and maintain and develop programs for use in business
- Most will specialise in a specific development field, such as mobile phone applications, accounting software, office suites or graphics software, and will have in-depth knowledge of at least one computer language
Additional Information
- Application developers work in a range of business sectors, including finance and the public sector. They often work as part of a team with other IT professionals, such as software engineers and systems analysts, and write programs according to their specifications.
- Their main function is to make computers perform specific tasks, based on the client’s specification. They will need to establish a detailed program specification through discussions with the client (clarifying the requirements), break the specification into its simplest elements and translate the logic into a programming language (e.g. Java), combine all elements of the program design and test it, and install the program into production. An evaluation of the system will also be carried out with the aim of increasing the program’s effectiveness.
- They will also work on updating, repairing, modifying and developing existing software.
-
Web Developer role
- Web developers build and maintain websites and web applications
- A web developer's primary task is creating reliable and high performing applications and services, which can be accessed over the internet
Additional Information
- A Web Developer may focus more on the interface and the visual design or may be involved in the whole thing (i.e. including the back end database and the underlying software).
-
Global projects
- 'global world where everyone can be connected'
- Issues when working on global projects
- Communications
- Trust
- Common working practices
- Tools
Additional Information
- Communication: be aware of different time zones and holidays..
- Trust: it is important to start building trust quickly by recognising and respecting team members differences and value added to the project.
- Common working practices/Tools: It is important to align work processes to the way the team operates in order for all team members to be comfortable in their project work. Time may be required to allow the team to develop common working practices using specific tools. For example, may share a common software platform with all team members e.g. collaborative project management software that team members can access on their own timeframe. May need standardised communication tools e.g. where team members use the same instant messaging software or chat tool. May need to regular ‘check ins’ with team members e.g. weekly skype calls/conference calls
-
Outsourcing/Offshoring
- Outsourcing: when an organisation acquires goods and/or sources from an outside source
- Offshoring: outsourcing to another country
- Project managers will need to
- Negotiate contracts
- Work/manage virtual teams
Additional Information
- Outsourcing – when an organisation acquires goods/services from an outside source. The term offshoring is sometimes used to describe outsourcing to another country. Offshoring is a natural outgrowth of globalisation and IT projects continue to rely more and ore on on-sourcing, both within and outside of their country boundaries.
-
Advantages of Virtual Teams
- 1. Improved efficiency by having a team of workers available 24/7
- 2. Lowered costs – many workers do not require office space (home workers)
- 3. Increases expertise & flexibility
- 4 . Increased work/life balance for team members (home workers)
Additional Information
- Increased globalisation and outsourcing have increased the need for virtual teams. Virtual Team: a group of individuals who work across in different areas using communication technologies.
- May be in the same company in the same country or they might include employees, consultants, contractors, etc. from around the world. Like any team the virtual team should focus on achieving a common goal.
-
Disadvantages of Virtual Teams
- 1. Isolated team members may not adjust well to working in a virtual environment
- 2. Increased potential for communications problems since teams may never meet
- 3. Reduced ability for team to network and transfer information informally
- 4. Increased dependence on technology to accomplish work
-
Virtual teams – factors for success (ref Schwalbe 2010)
Research on virtual teams reveals a growing list of factors that influence their success including:
- Team processes must be defined
- it is important to define how the team will operate, when & how work will be done, how decisions will be made and what technologies will be used
- Leadership style
- Project manager’s leadership style affects all teams especially virtual teams
- Trust and relationships
- Many virtual teams fail due to lack of trust
- May need to use phone/video conferencing
- Team member selection and roles
- Virtual team must cover all roles
- Task- technology fit
- Cultural differences
- In terms of communication & decision making
- Computer mediated communications
- Must be reliable and appropriate for the virtual team
- Team life cycles – must be considered in terms of:
- Assigning team members
- Determining deliverable schedules
- Incentives
- Provide frequent positive incentives e.g. thank you email
- Negative incentives: payment withholding/fines
- Conflict management
Additional Information
- Conflict management
Even thought they never meet, Virtual teams can still have conflict. It is therefore important to address conflict management