01
-
-
Industrial Strategy: Building a Britain fit for the future
- Published at end of 2017 by the UK government.

-
Four Grand Challenges for the industries of the future:

-
Data Economy highlights
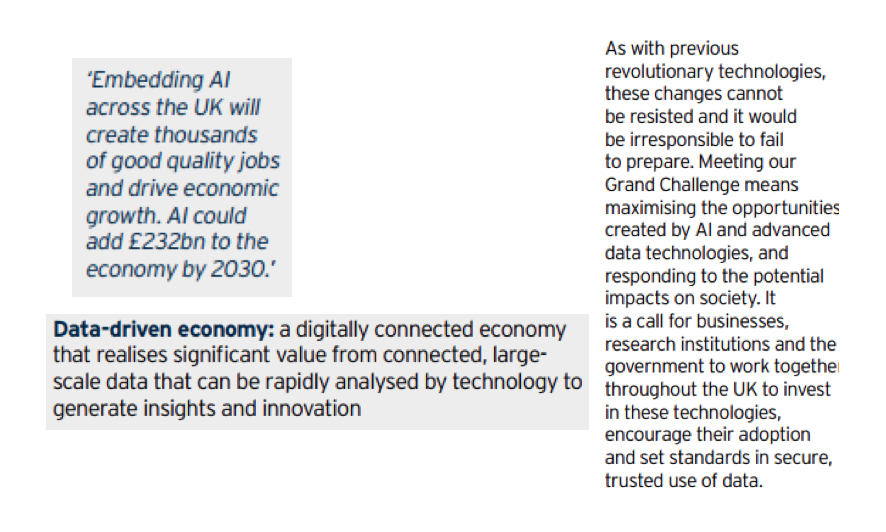
-
Summary of the module content
- Aim: allow the students to develop the analytical skills required to analyse and interpret data in an engineering context.
- Theory: the module will use probabilistic, statistical, Fourier and modelling methods to give the students the ability to meaningfully abstract information and make inferences from their data.
- Practical approach: in conjunction with the theoretical aspects of data analysis, this module will also provide the students with the appropriate implementation strategies to perform their data analysis using MATLAB software.
Lectures, tutorials, labs
- Lectures: Concepts in probability theory, linear algebra, data modelling and data analysis, applications with plenty of solved examples, MATLAB with concepts and solved examples.
● Electronic version on GCU Learn
- Tutorials: Problem solving by students & understanding of the theory
● Electronic version on GCU Learn
- Labs: MATLAB software – concepts and practical use for computation on vectors and matrices, plotting, linear algebra solutions, random number generation, filtering, smoothing, frequency analysis, regression.
● Electronic version on GCU Learn
Module structure
- Two hours of lectures per week
● Concepts and solved problems from probability, linear algebra, data modelling and data analysis- One hour tutorial each week
● Problem solving and understanding of the theory- Two hours of lab per week
● MATLAB software is used for computation, plotting, data modelling, data analysis, data smoothing, Fourier analysis
Assessment
- Exam (50%)
● Mock exam provided near the end of the semester.- Coursework (25% and 25%)
● Mid semester (25%) and end of semester (25%) GCU Learn-based assessment
● Multiple choice based assessment of Matlab skills
Reading
- Counting, Probability and Statistics and concepts
- “Probability and Statistics”; John J. Schiller, R. Alu Srinivasan, Murray R Spiegel, 3rd Edition, 2009 (or 4th edition, 2013)
- Optional MATLAB book:
- “Introduction to MATLAB for Engineers”, Third Edition, William J. Palm III, 2010
-
Theoretical Concepts from Probability - Topics
- Probability, Axioms, Distributions:
- Random experiments, Sample Space, Sample Point, Discrete Events, Set Operations on Events, Probability – Classical and Frequentist Approach, Axioms of probability, Sum and Product Rule, Independence, Joint Probability, Conditional Probability, Bayes Rule, Probability Distributions (Binomial, Uniform, Poisson, Bernoulli), Gaussian distribution and z-score
MATLAB and Theory Topics
- Linear Algebra: Matrices and vectors, multiplication and addition, transposition, inverse matrices
- Data Analysis: Removing and interpolating missing values, removing outliers, filtering (smoothing and shaping data) – moving average, median filter, de-trending data, robust statistics (trimmed mean, Winsor mean), data trending and visualisation
- Data Modelling: Correlation analysis, correlation coefficient, covariance, cross correlation and autocorrelation, linear regression
- Fourier Analysis: Sampling, Time domain to frequency domain using FFT, magnitude and phase, zero padding, harmonic analysis, power spectrum, spectrum analysis
Learning Outcomes
- Construct and simulate probabilistic models for various random phenomena
- Successfully select and apply appropriate data smoothing methods to remove noise from data
- Apply correlation and regression methods to explore relationships between time series data
- Understand and utilise frequency domain concepts to extract information from data
- Implement the above methods using a suitable software package such as Matlab
Teaching and Learning Strategy
- This course focusses predominantly on improving the analytic data analysis skills of the students: appropriate mix of theoretical and practical implementation is required.
- The theoretical material will be introduced through lectures, with the implementation being introduced via practical exercises involving real world contextualised problem solving. Tutorials will be used to explain and elaborate on the lecture material and laboratory exercises.
- To ensure the module is industrially relevant for each programme, real world case studies will be utilised within the laboratories to reinforce the theoretical concepts and expose the students to open ended engineering problems.
- Full use will be made of GCU Learn to provide Lecture-based and related study materials, along with sample solutions of Tutorial and Laboratory exercises, thus encouraging the development of independent learning and allowing self-reflective feedback on student performance. Staff-based feedback on student performance for submitted work will be provided in line with the University feedback policy, with summative feedback and grades on the coursework assessment utilising GCU Learn.
Teaching approach (short version)
- A Chinese proverb states:
Tell me, I’ll forget
Show me, I’ll remember
Involve me, I’ll understand