-

-
Introduction
- Nowadays, power electronics has become an integral part of power systems and industrial processes.
- This has become more significant with the rising technology in power semiconductor devices and their capabilities
- Polarity of voltage blocked and direction of current conduction
- Switching speeds and power ratings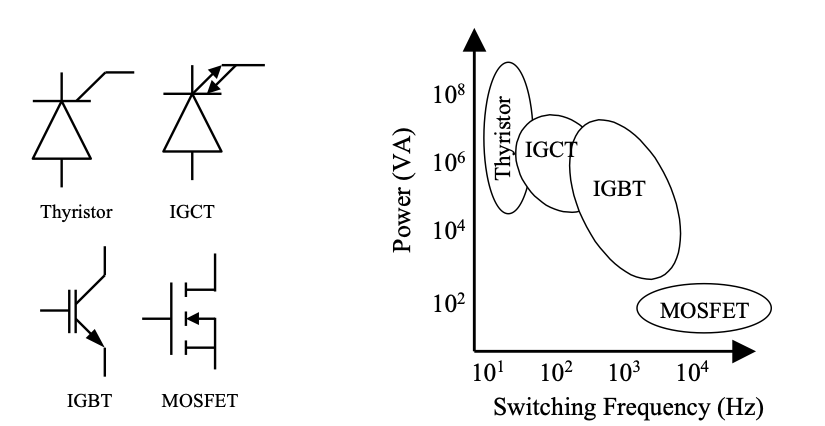
- Among the applications of power electronics systems are:
1. High Voltage DC Transmission (HVDC) systems.
2. Renewable Energy & Distributed Generation Systems.
3. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) & Energy Storage.
4. Adjustable Speed Drives. -
1. HVDC systems
Grid Tie HVDC systems
DC Transmission is the most flexible solution for connection of two AC systems (especially with different frequencies- asynchronous interconnection) e.g. grid tie between 60Hz grid in Brazil and 50Hz grid in Argentina
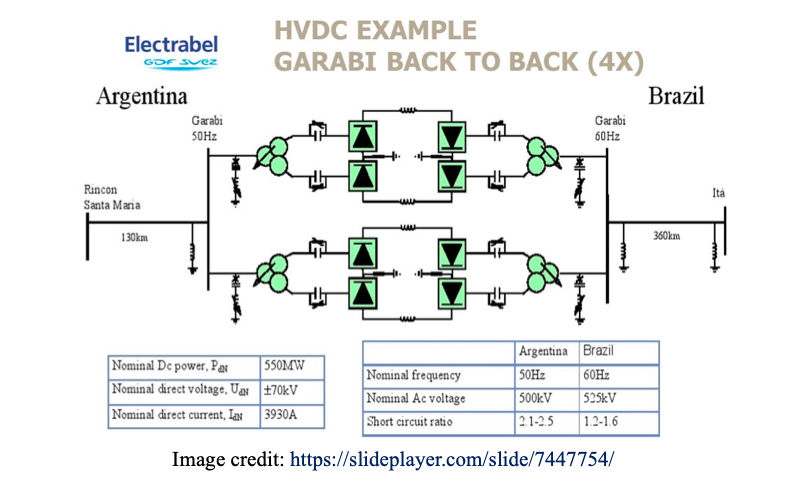
Types of HVDC Systems
HVDC systems are generally either:
- Current-source based (DC link current controlled)
- Voltage-source based (DC link voltage controlled)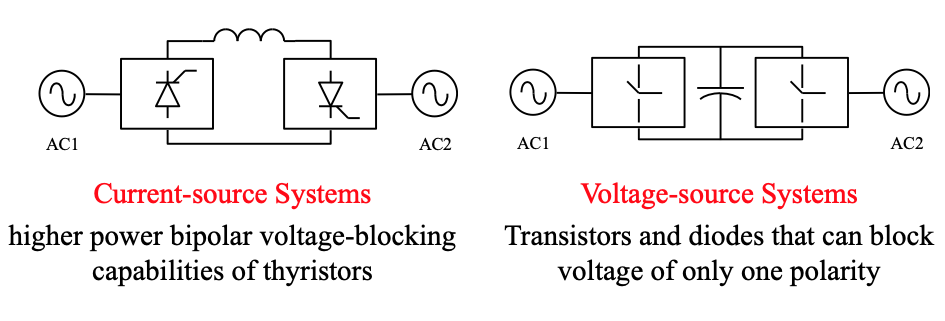
-
2. Renewable Energy & Distributed Generation Systems
Evolving energy generation
The source of energy is evolving……
Distributed Generation
Power systems are also evolving. Rather than only centralized power generation in bulk power stations, more decentralized sources of energy are emerging, e.g. rooftop photovoltaics, local wind farms….etc. This is known as distributed generation (DG).
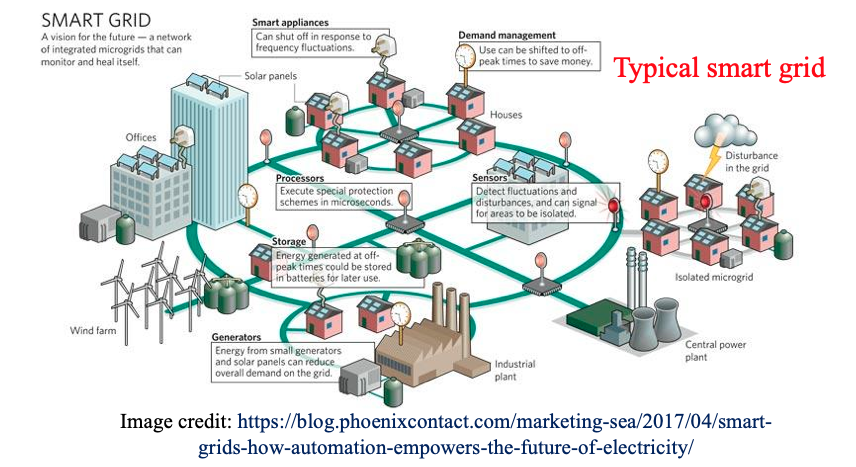
Renewable Energy Systems
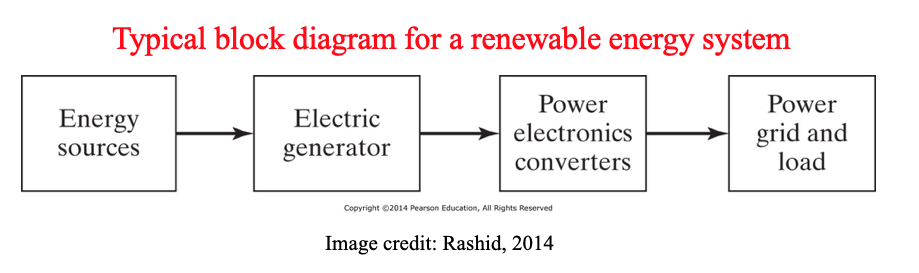
- Power electronic converters used for DG systems depend on the source of energy (wind, solar, marine, fuel cell…..etc)
- Here, we will focus on Wind and Solar systems.
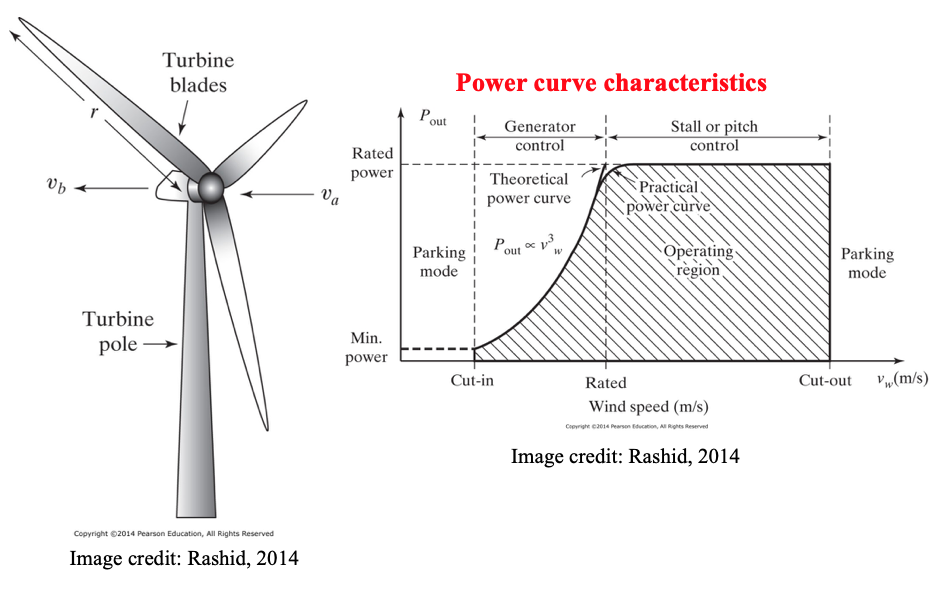
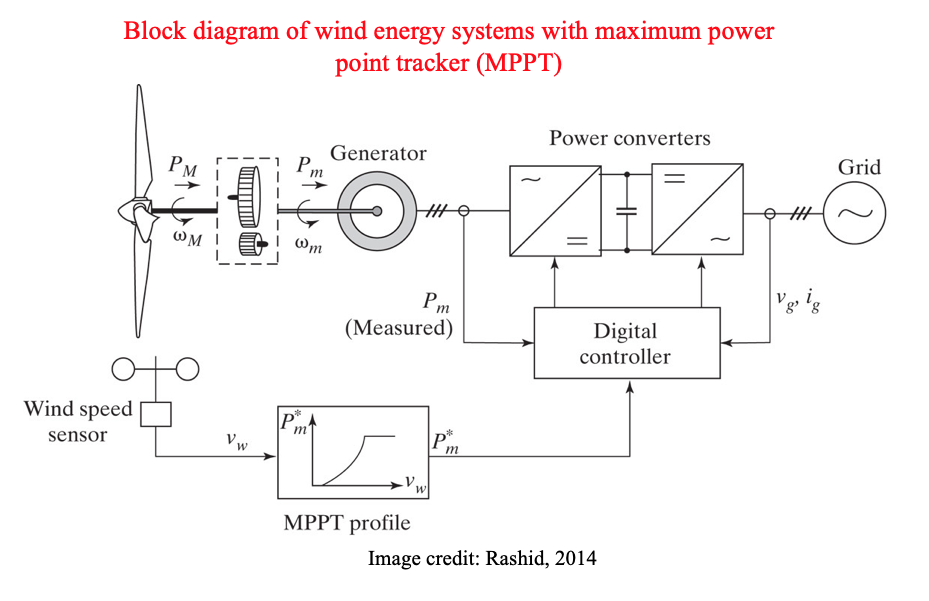
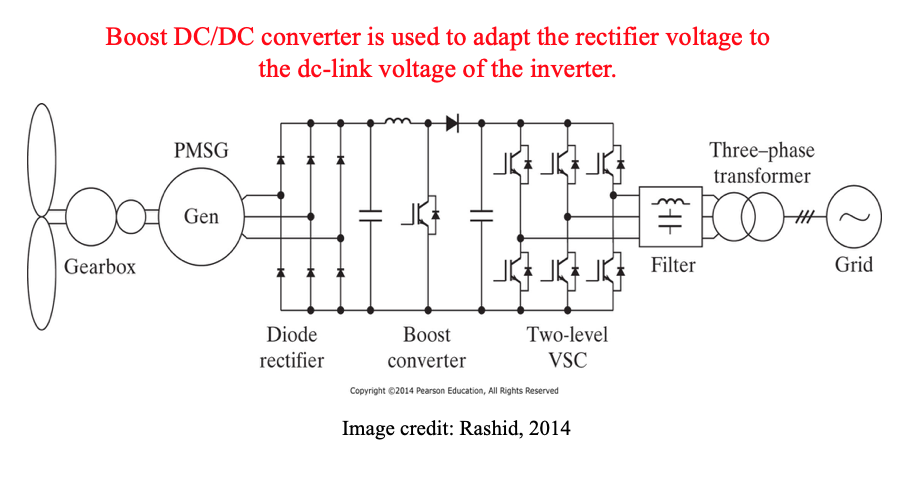
Wind Energy Systems
- Wind power has a great potential to supply the globe with electricity. We need to have 300,000 nuclear power stations on earth to generate as much power as what global wind can produce!
- In the UK, one of the best locations for wind power in the world, the operational wind capacity was 16.1 GW in August 2017 providing electricity for an equivalent of 10.7 million homes per annum
- The output of wind generation is intermittent, while grid connection needs voltage and frequency to be well regulated
- This cannot be done without power electronics!
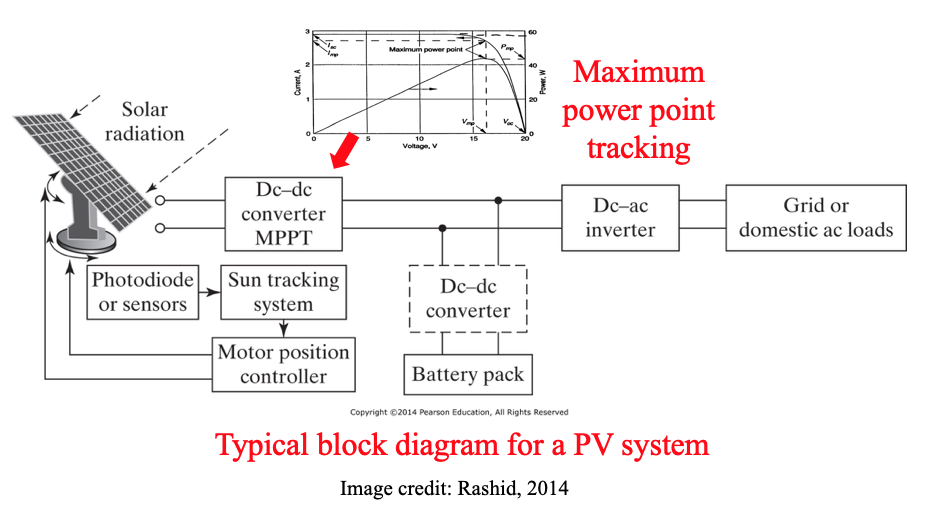
Photovoltaic (PV) systems
- This is more power hitting the Earth from the sun in a single hour than humanity uses in an entire year!!
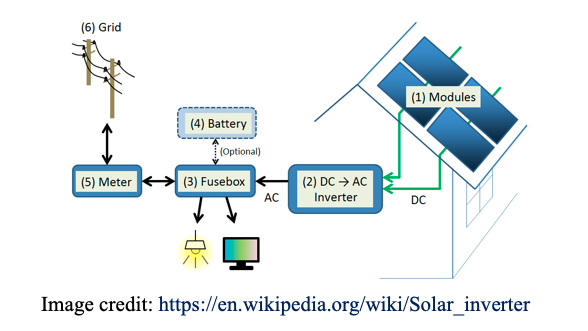
- Photovoltaics is the direct conversion of sunlight to electricity
- The electrical output of the PV panel is DC - converted to AC (needs power electronics)..
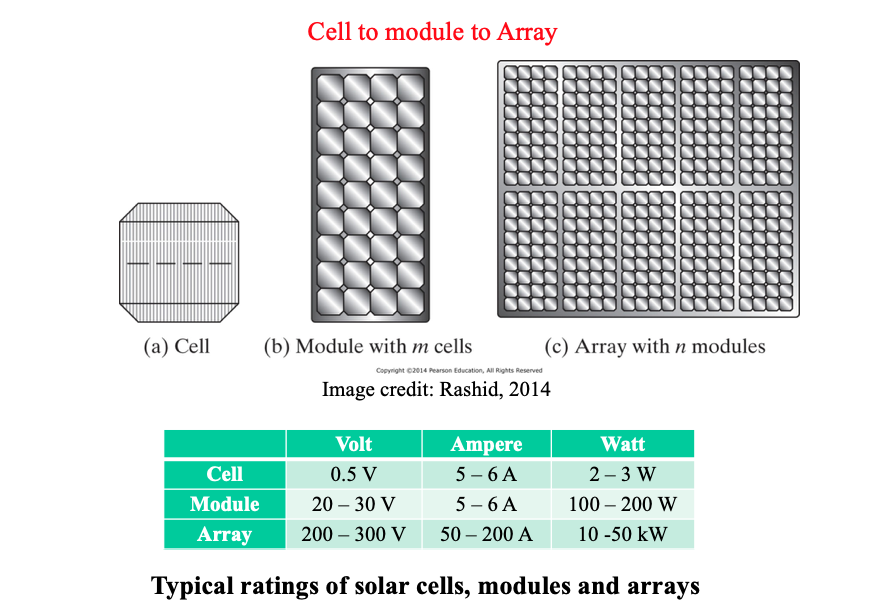
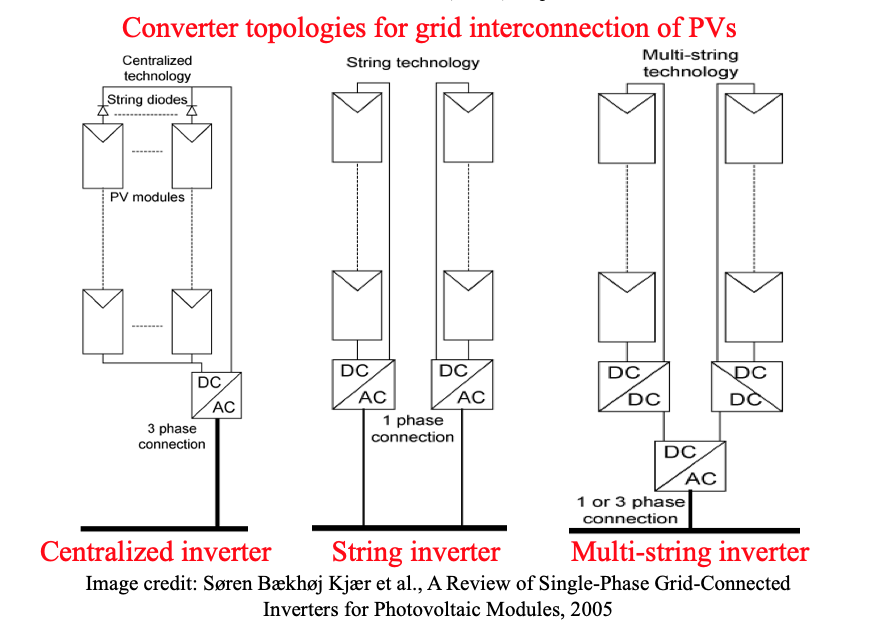
- Centralized inverters:
- PV modules as series connection (s string), then connected in parallel through string diodes.
- Losses in string diodes, HVDC cables between PV modules and inverter, power losses due to centralized MPPT controller.
- String inverters:
- Reduced version of centralized inverter
- Single string of PV modules connected to inverter
- No losses on string diodes
- Separate MPPTs
- Increases overall efficiency
- Multi-string inverters:
- Flexible (open for parallel addition)
- Every string can be controlled individually
- DC voltage boosting
- Common DC-AC inverter -
3. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) & Energy Storage
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
- UPS is pivotal for critical loads that cannot afford any mains outage, e.g. hospital intensive care units.
- These need energy storage as a back up unit to ensure continuous supply in case of mains outage.
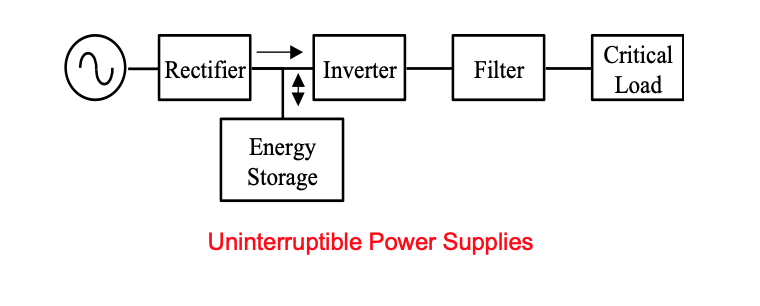
Energy Storage
- Also, almost all renewable sources are intermittent. At night, PVs do not generate electricity. Wind is also quite varying.
- For loads to be regulated at constant voltage and frequency from such intermittent sources, energy storage is one of the solutions.

-
4. Adjustable Speed Drives
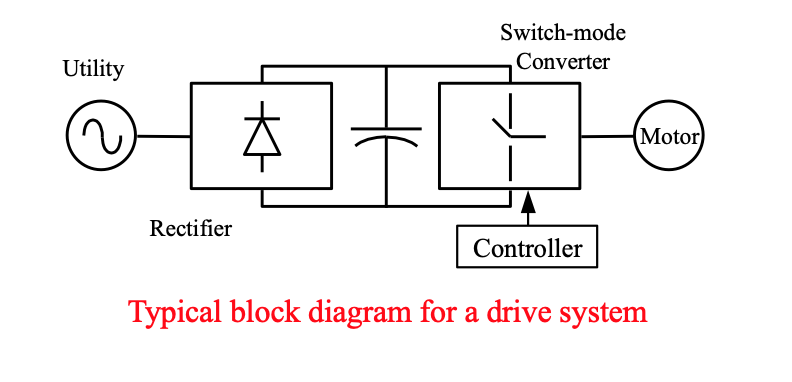
Electrical Drive Systems
Adjustable speed drives are the electric motor control systems which facilitate the motors’ operation at variable speed/torque according to the requirements of the mechanical load they are driving.
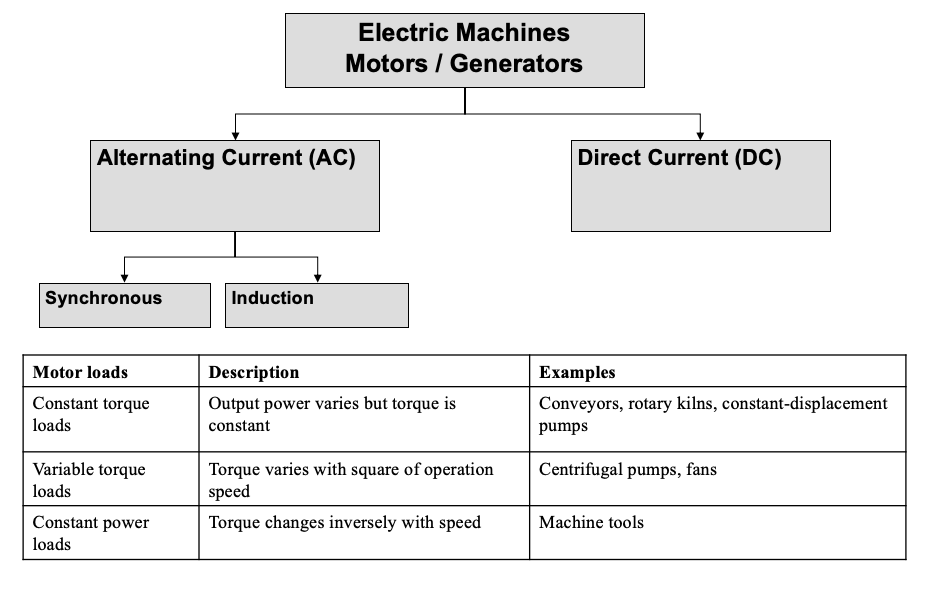
Electrical machines and mechanical loads
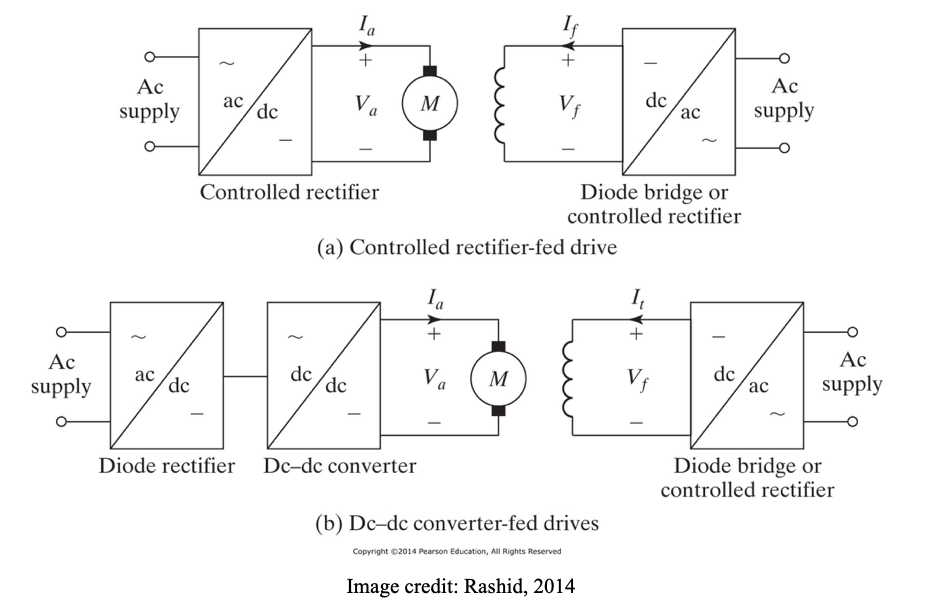
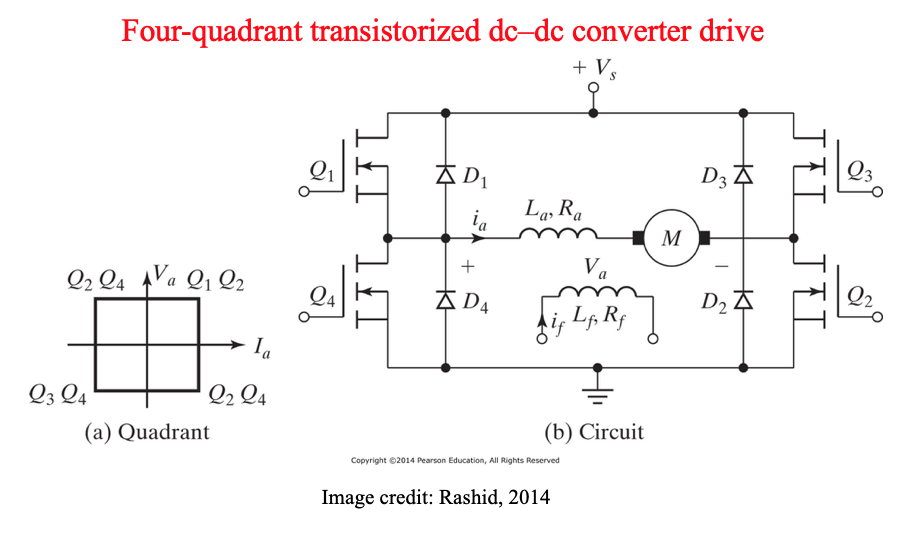
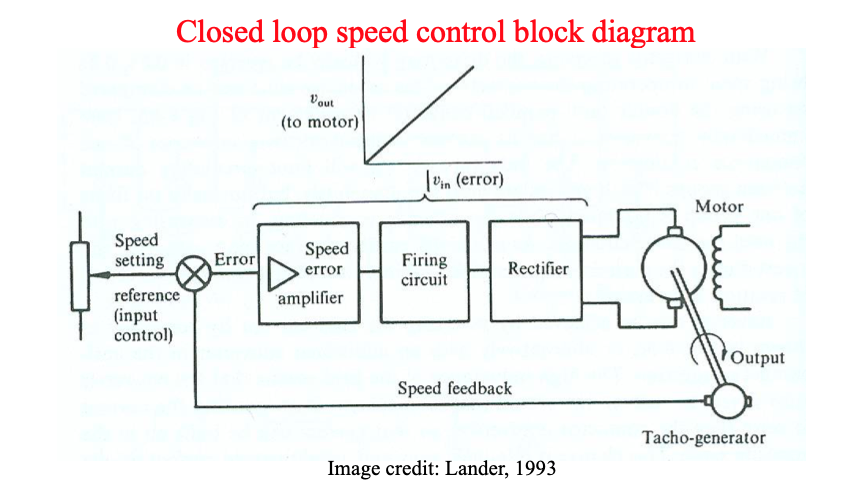
DC Drives (DC motor speed control)
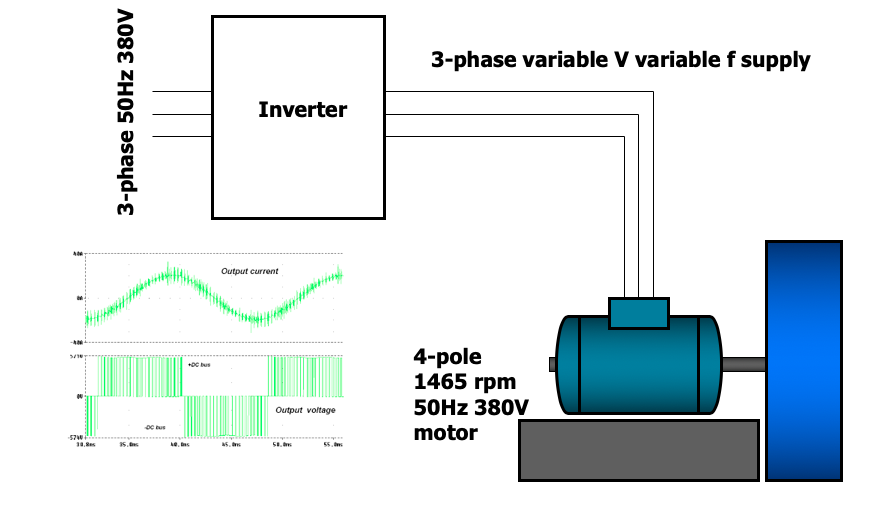
AC Drives (Induction motor speed control)
-
Check your understanding by answering the following:
- With the aid of a graph of power rating vs switching frequency, explain the capabilities of the following semiconductor devices: Thyristors, MOSFETs and IGBTs.
- With the aid of block diagrams, discuss the following application areas of power electronics:
• HVDC systems
• Distributed generation wind energy systems.
• Distributed generation photovoltaic systems.
• Uninterruptible power supplies.
• DC motor variable speed control.
- Your answer should describe the operating principles employed and a specific example of the typical power electronics used.